Content
Direct Answer: Is Die Cast Healthy and Safe?
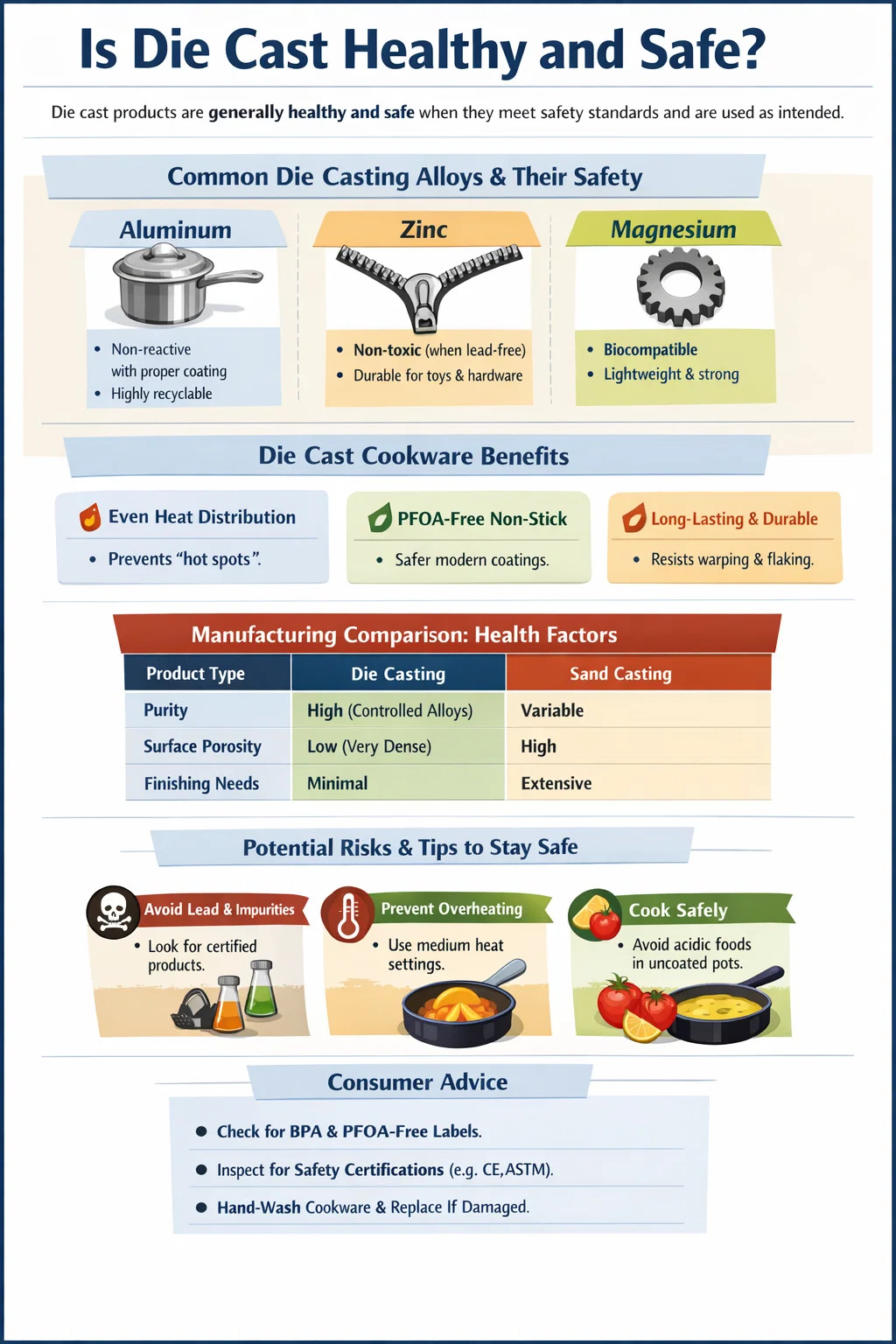
Generally speaking, products made through die casting are considered healthy and safe for everyday use, provided they meet international safety standards and are used as intended. The "healthiness" of a die cast item depends primarily on the base metal used (such as aluminum, zinc, or magnesium) and the surface treatment applied to it. In the context of cookware, die cast aluminum is highly popular because it is non-reactive when properly coated, while in toys and hardware, die cast zinc is favored for its durability and lack of toxic additives like lead.
However, consumers should be vigilant about the purity of the alloys and the quality of non-stick coatings (like PTFE or ceramic), as low-quality manufacturing can lead to the leaching of heavy metals or chemical fumes if the product is overheated.
Safety Profiles of Common Die Casting Alloys
The metals used in the die casting process vary in their biological interaction. Understanding these alloys is the first step in assessing health risks.
Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminum is the most common metal for die cast kitchenware. While there have been historical concerns regarding aluminum and neurological health, modern die casting aluminum products are usually sealed with an anodized layer or a high-grade coating. This prevents raw aluminum from leaching into food. Aluminum is also highly recyclable, making it a "healthy" choice for the environment.
Zinc Die Casting
Zinc alloys (often called Zamak) are primarily used for hardware, zippers, and toys. Zinc is an essential mineral for the human body, and die cast zinc is non-toxic. The main health concern with zinc products isn't the zinc itself, but the potential for lead contamination in low-grade alloys. Reputable manufacturers ensure lead content is below 90 parts per million (ppm) to comply with global toy safety regulations.
Magnesium Die Casting
Magnesium is incredibly light and used in medical implants and high-end electronics. It is biocompatible, meaning the body generally tolerates it well. In a die casting context, it is safe to handle and does not pose respiratory or skin health risks once cast into a solid form.
Die Cast Cookware: Heat Distribution and Chemical Safety
When people ask "is die cast healthy," they are usually referring to pots and pans. Die cast cookware is made by pouring molten aluminum into a permanent mold, resulting in a thicker, sturdier pan compared to stamped aluminum.
- Uniform Heating: The thickness of die casting products prevents "hot spots" that burn food. Burnt food can contain carcinogens like acrylamide, so even heat distribution is a tangible health benefit.
- Non-Stick Coatings: Most die cast pans use a coating. Modern pans are PFOA-free, which is a significant health upgrade over older generations of non-stick technology.
- Durability: Unlike cheap pans that warp and flake, die cast items maintain their integrity, reducing the risk of consuming coating particles.
Comparison of Casting Methods and Health Impact
How does the die casting process compare to other manufacturing methods in terms of safety and purity? The table below highlights the key differences.
| Product Type | Die Casting | Sand Casting | Health Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purity | High (Controlled Alloys) | Variable | Less risk of impurities. |
| Surface Porosity | Low (Very Dense) | High | Prevents bacteria buildup. |
| Finishing Needs | Minimal | Extensive | Fewer chemical cleaners used. |
Potential Risks and How to Mitigate Them
Despite the general safety of die casting, there are specific scenarios where health risks might arise. Awareness is the key to mitigation.
Heavy Metal Impurities
In unregulated markets, scrap metal may be used in the die casting process. This can introduce lead, cadmium, or arsenic. To stay healthy, always purchase die cast products that carry certifications like FDA approval for food contact or RoHS compliance for electronics and toys.
Overheating Aluminum Cookware
While die cast aluminum is a great conductor, heating an empty pan to temperatures above 260°C (500°F) can cause non-stick coatings to decompose. This releases fumes that can cause "polymer fume fever." Always use medium heat settings with die cast pans.
Leaching in Acidic Environments
If you are using an uncoated die cast aluminum pot, avoid cooking highly acidic foods like tomatoes or citrus for long periods. The acid can react with the metal, resulting in a metallic taste and increased aluminum intake.
Constructive Advice for Consumers
To ensure your experience with die casting products remains healthy, follow these practical steps:
- Check for BPA and PFOA-free labels on all die cast cookware.
- Inspect toys and hardware for the CE mark or ASTM F963 certification, ensuring the die cast zinc is lead-free.
- Hand-wash die cast pans even if they claim to be dishwasher safe; harsh detergents can degrade the protective coatings over time.
- If a die cast item shows signs of deep scratching or flaking, it is time to replace it to avoid ingesting particles.
In conclusion, die cast products are a triumph of modern engineering. They offer safety, longevity, and performance. By choosing high-quality items and following basic care instructions, you can enjoy the benefits of this versatile manufacturing process without compromising your health.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español










