Die Casting Explained
1. Core Essence
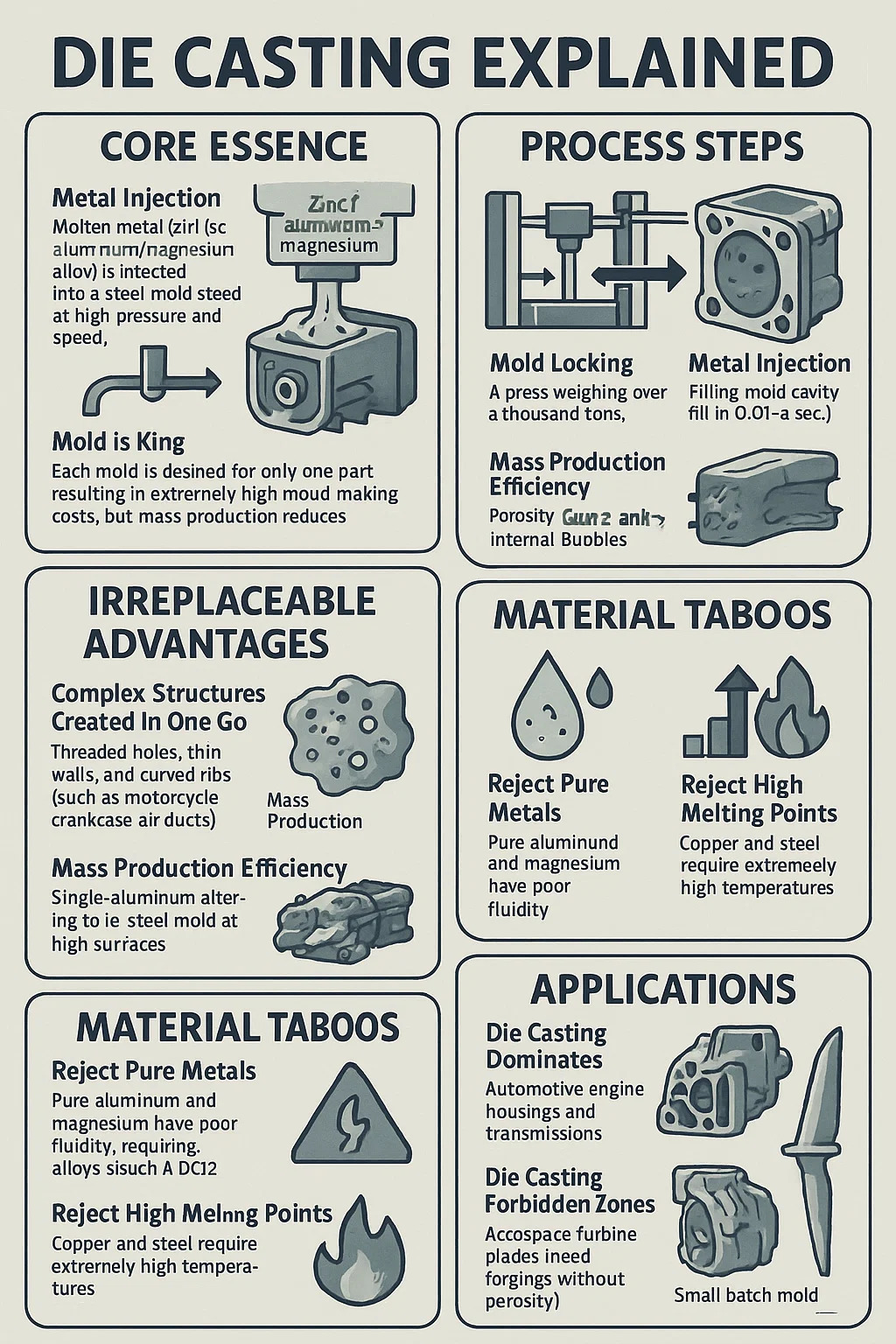
Metal Injection Molding: Molten metal (zinc/aluminum/magnesium alloy) is injected into a steel mold at high pressure and speed, and ejected after cooling to form the part.
Mold is King: Each mold is designed for only one part, resulting in extremely high mold-making costs, but mass production reduces the unit price.
2. Process Steps
Mold Locking: A press weighing over a thousand tons seals the steel mold tightly, ensuring it does not crack under high pressure.
Metal Injection: Liquid metal rushes into the mold cavity at cannonball speed (filling in 0.01-0.3 seconds).
Water Cooling and Solidification: Built-in water channels in the mold rapidly cool the part, solidifying it into shape.
Ejection: The ejector ejects the part, removing the runner waste (re-cutting is required).
3. Irreplaceable Advantages
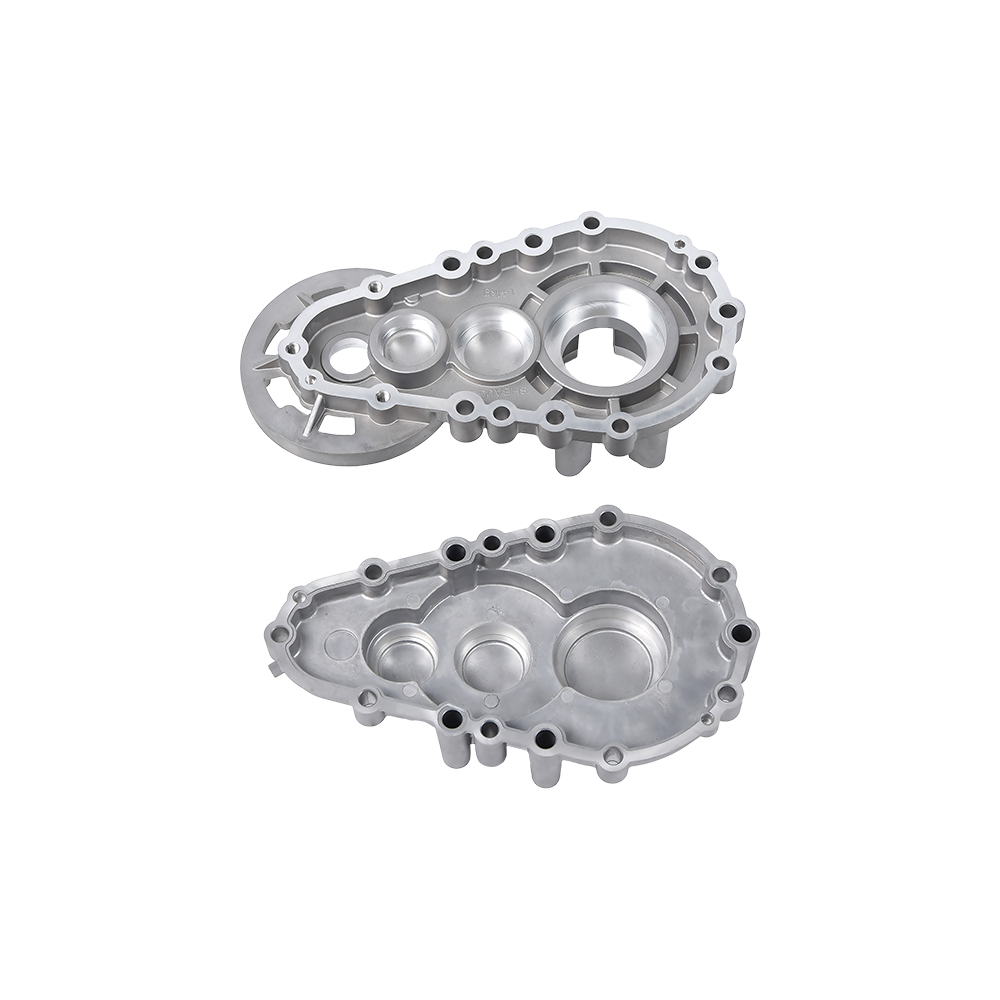
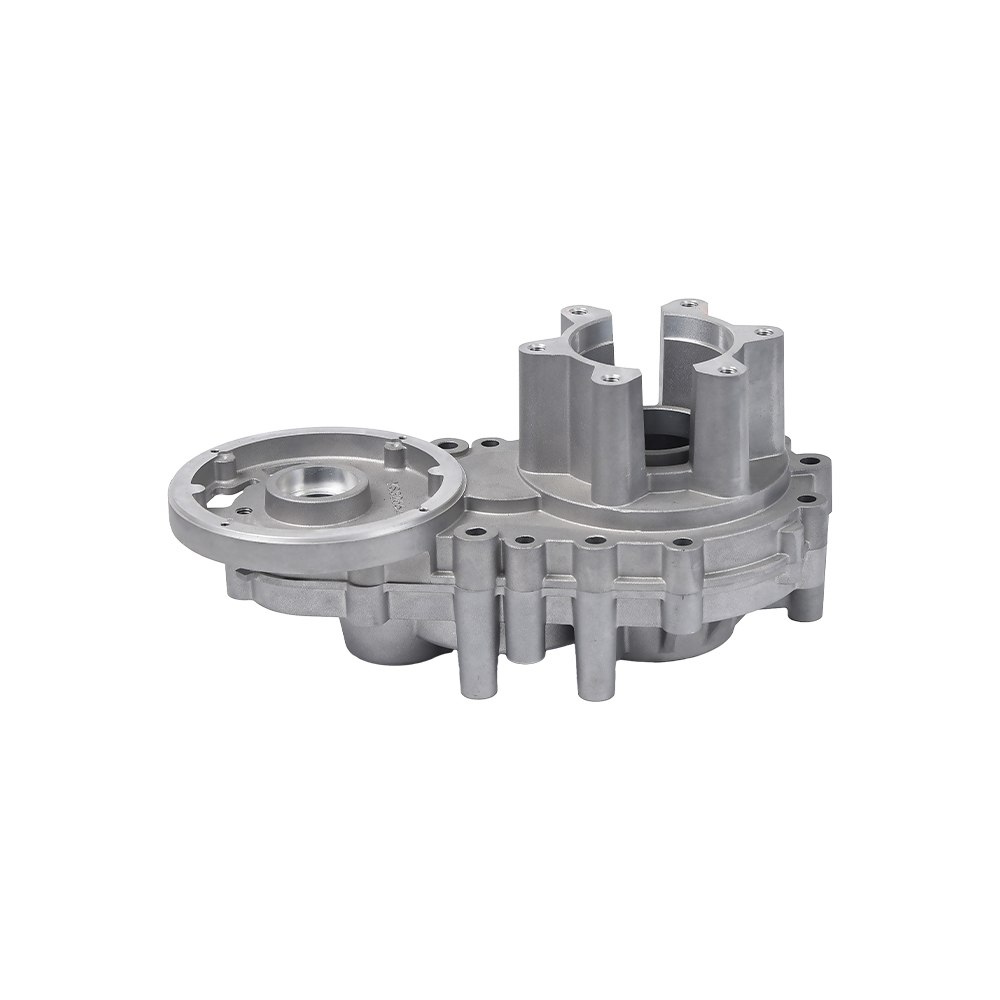
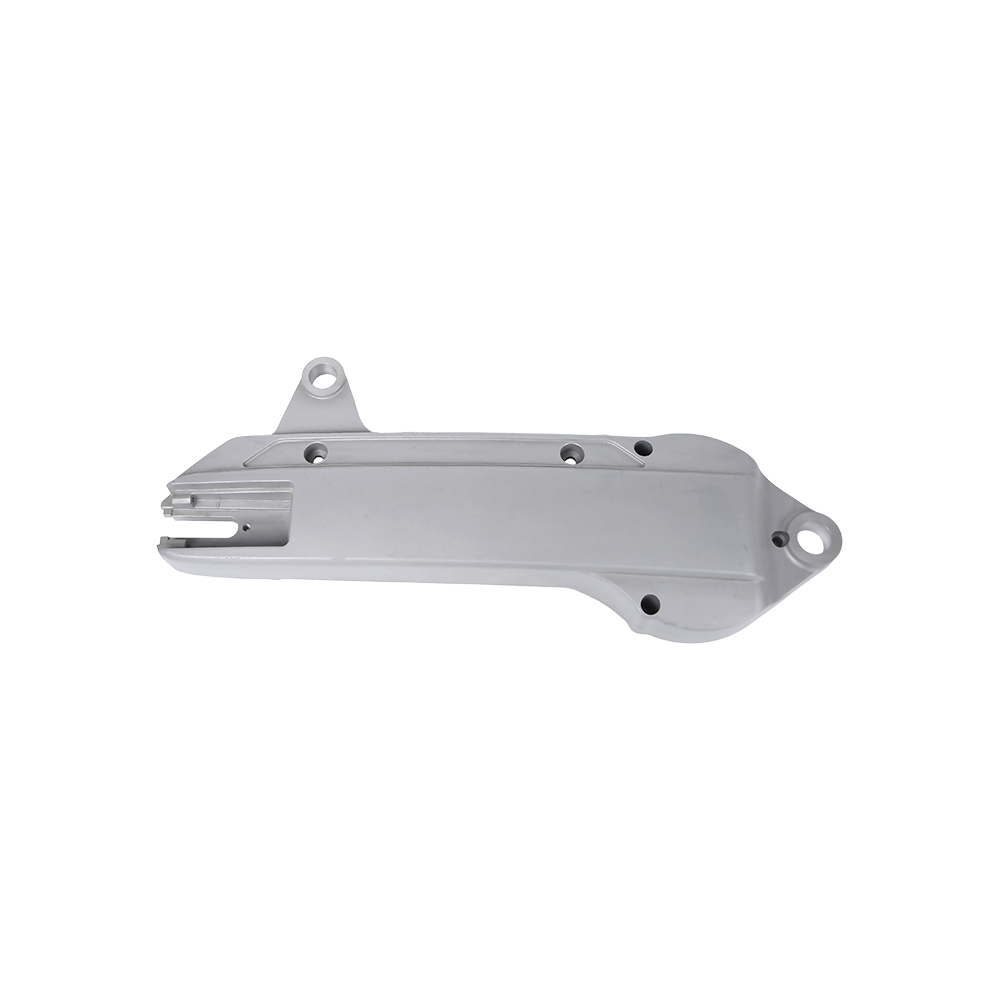
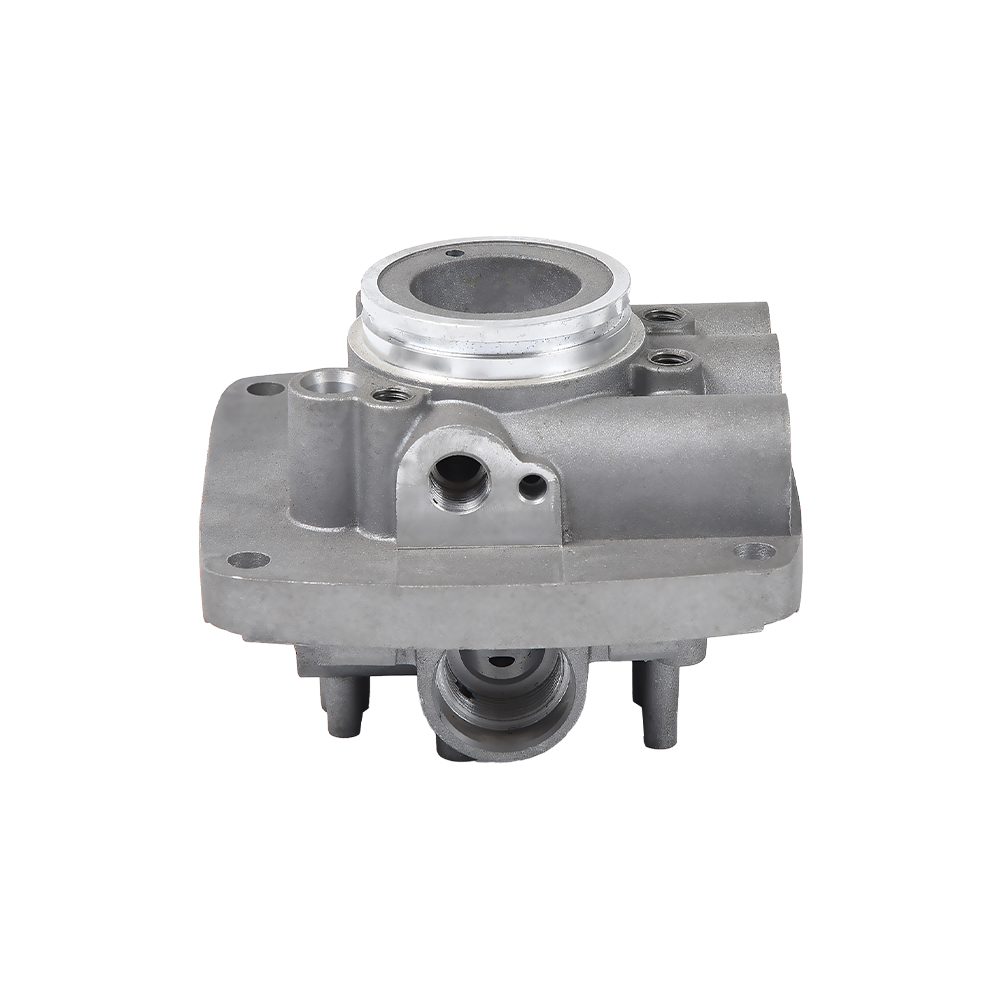
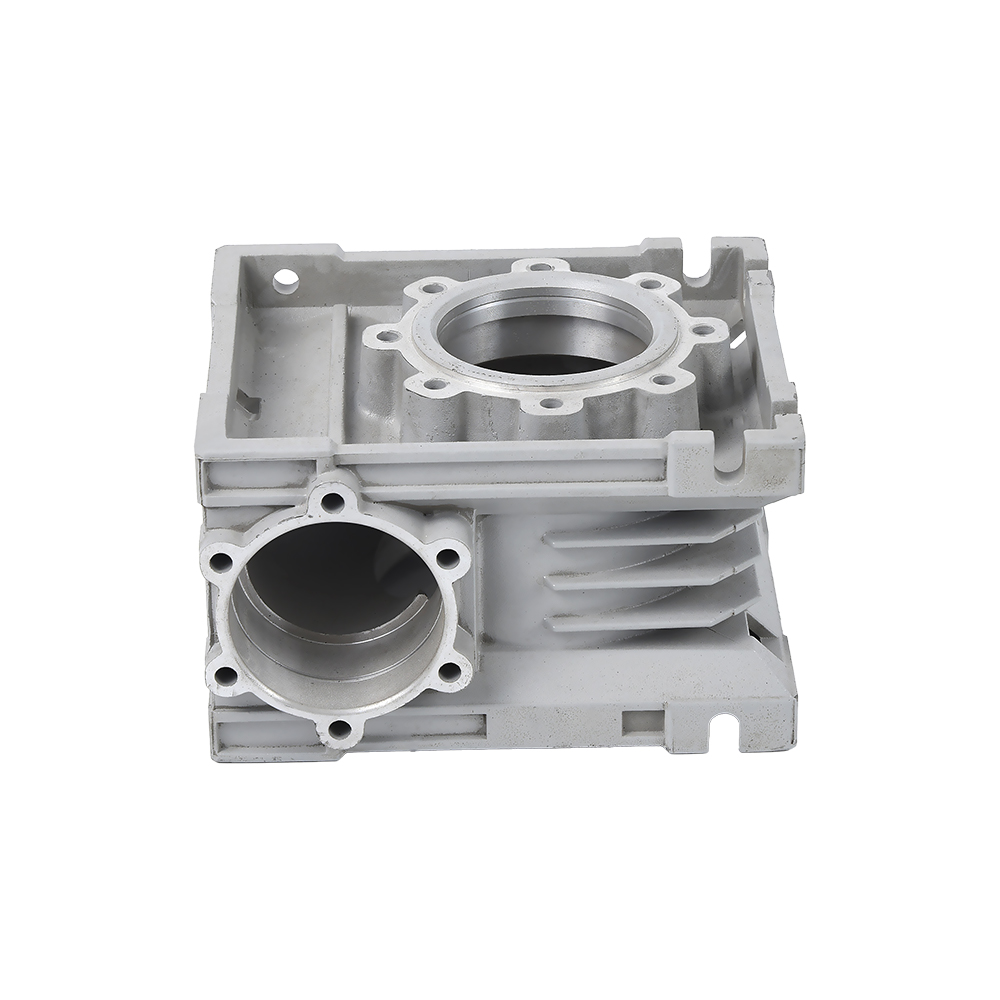
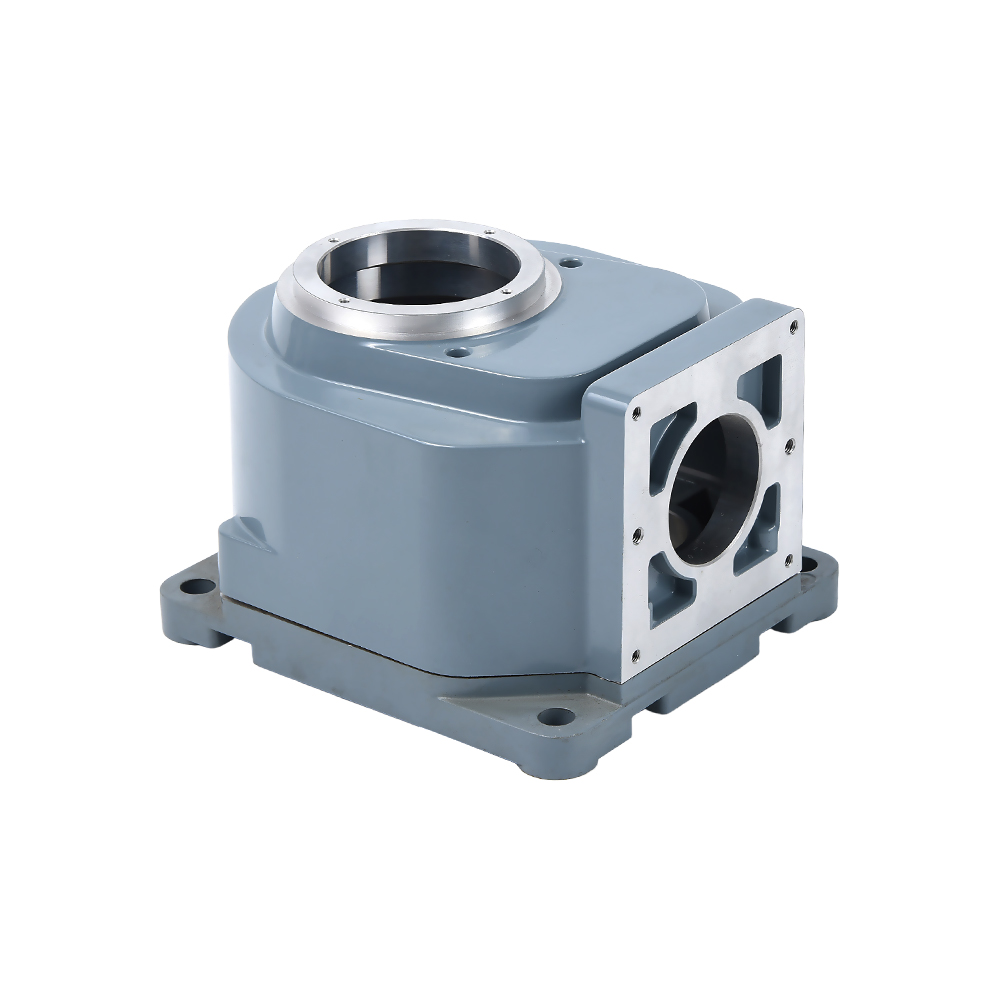
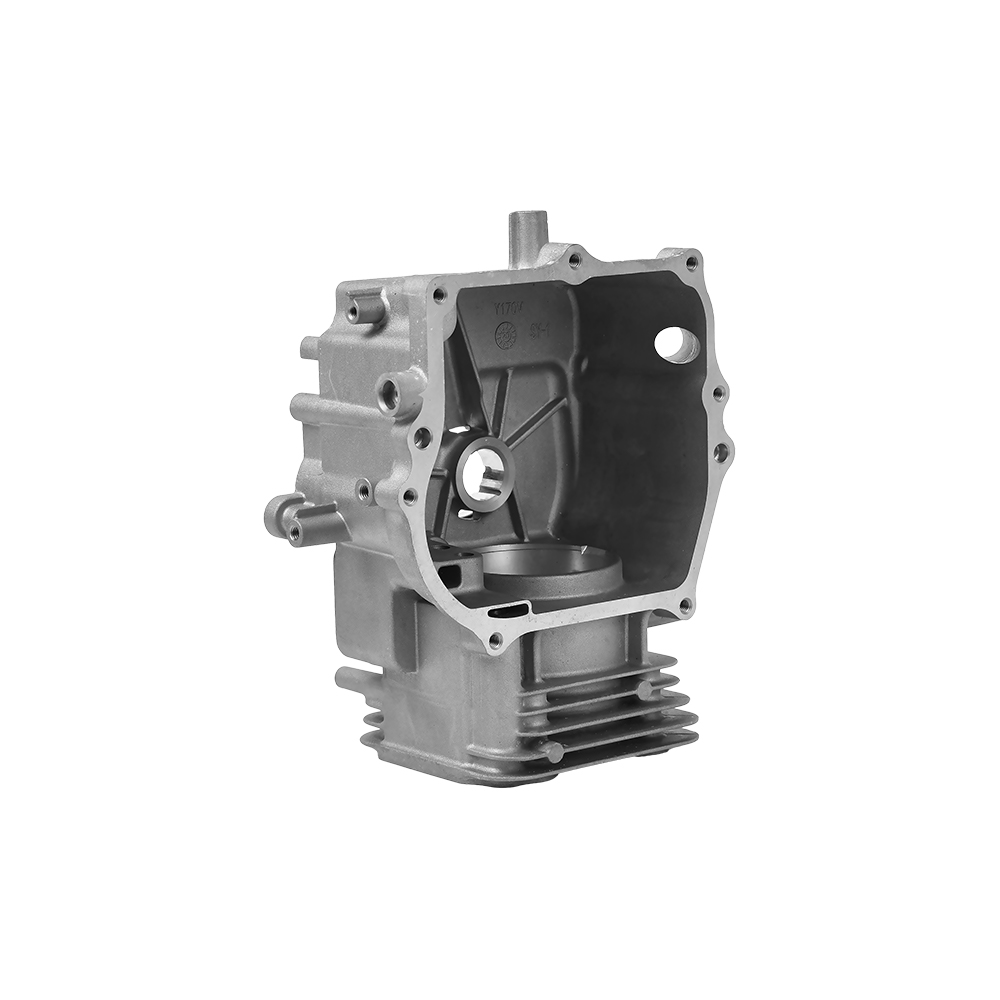
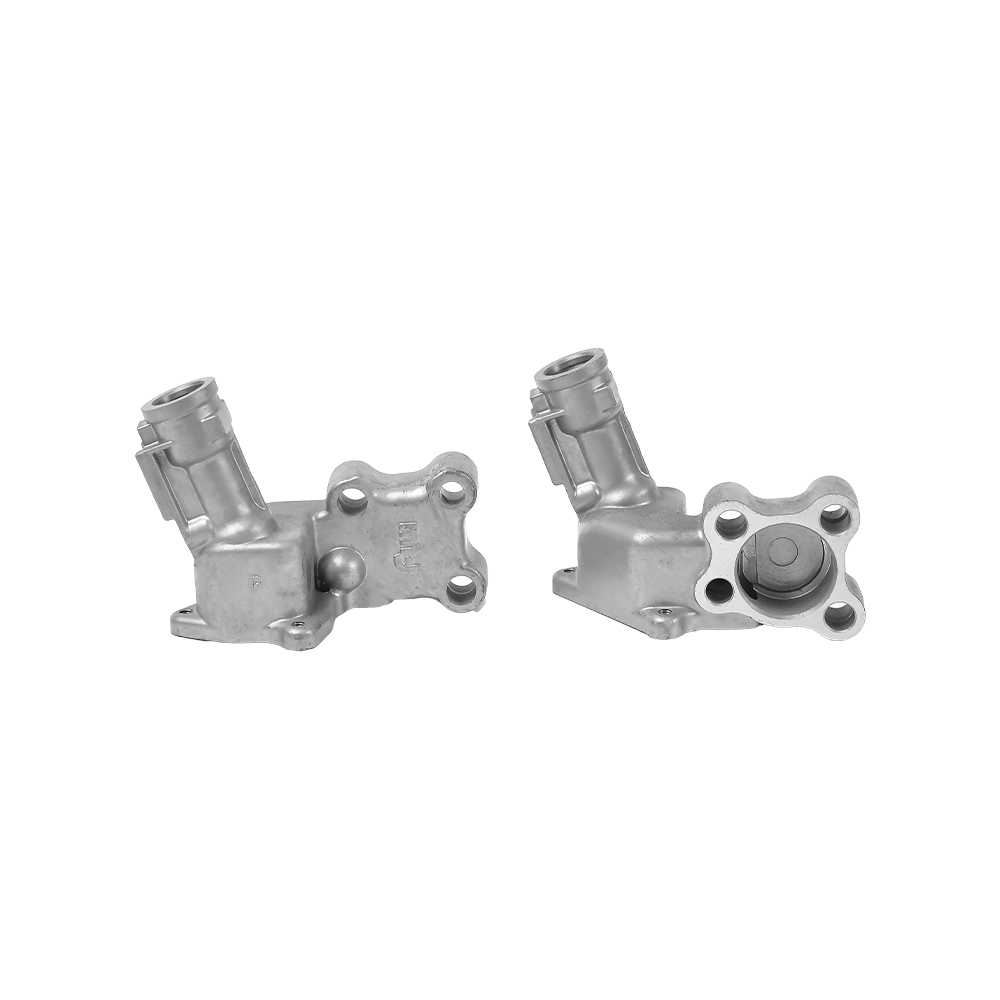
Complex Structures Created in One Go:
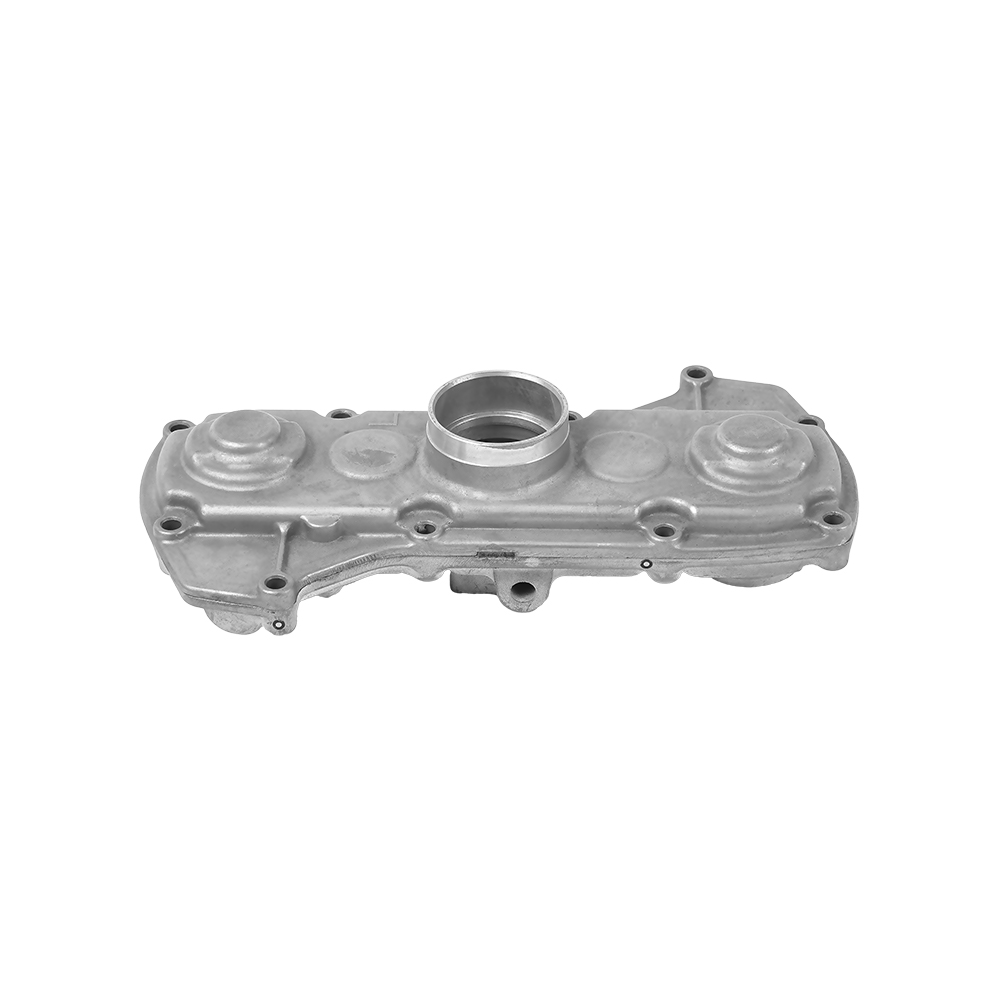
Threaded holes, thin walls, and curved ribs (such as those in motorcycle crankcase air ducts) can be formed.
Surface finish surpasses turning/forging, allowing for direct assembly. Mass Production Efficiency:
Single-part production cycle ≤ 1 minute, 24/7 uninterrupted material output.
4. Fatal Flaws and Countermeasures
Porosity: Air trapped under high pressure leads to internal bubbles in the part, resulting in a sharp drop in strength.
Solution: Vacuum re-injection (vacuum die casting) reduces porosity by half.
Mold Sticking and Burning: Molten aluminum adheres to the steel mold at high temperatures, resulting in tearing of the part surface.
Hard-Core Defense: Mold spraying with tungsten carbide coating increases mold life by 10 times.
5. Material Taboos
Rejecting Pure Metals: Pure aluminum and magnesium have poor fluidity, requiring alloys (such as ADC12 aluminum with 10% silicon).
Rejecting High Melting Points: Copper and steel die casting require extremely high temperatures, instantly rendering the mold useless.
6. Applications
Die Casting Dominates:
Automotive engine housings and transmissions (lightweight + complex oil circuits).
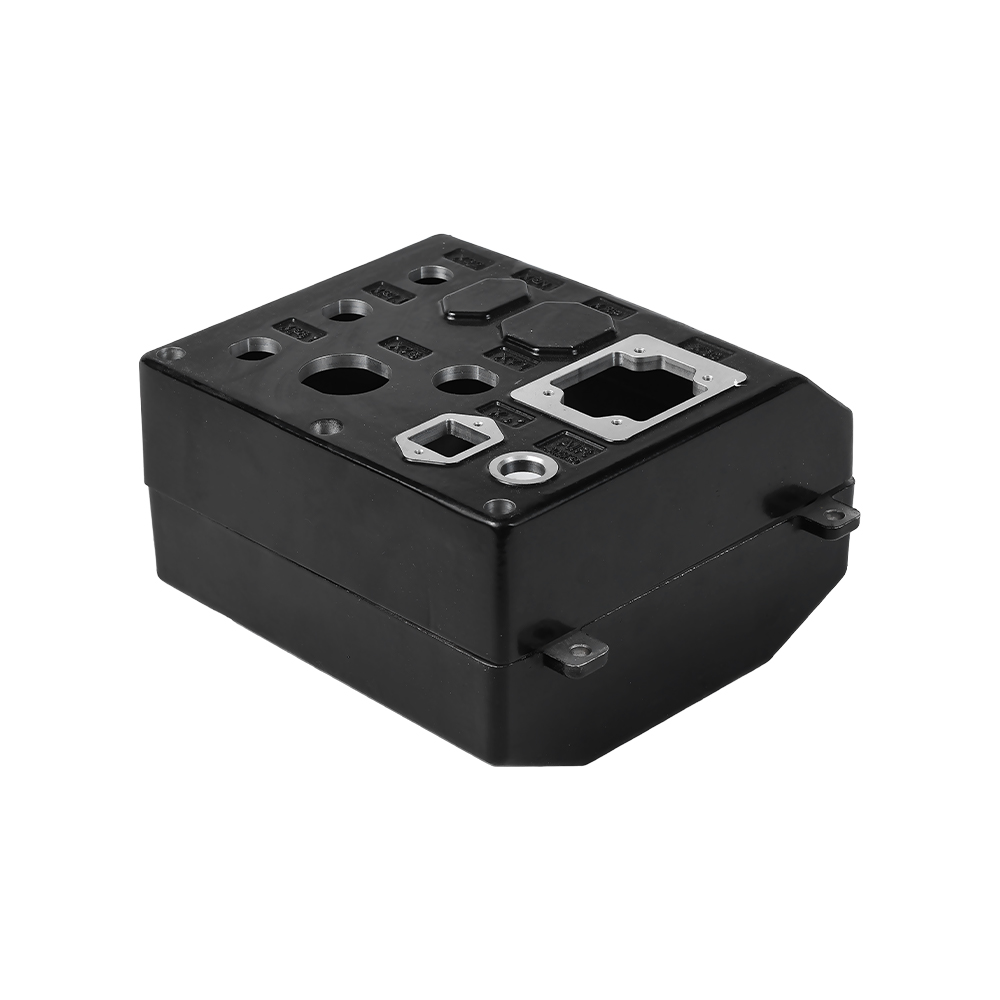
3C product housings (integrated antenna slots + cooling fins).
Die Casting Forbidden Zones:
Aerospace turbine blades (need forgings without porosity). Art sculpture (small batch mold making is a loss-making business).

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español










